A list of main components, scripts, 3d printing/laser cutting files, instructions
A brief introduction
A flight simulator is a specialised experimental setup designed for studying the orientation and navigation of flying insects. It serves as an analogue to Emlen funnels, which are widely used in avian research to investigate the orientation behaviour of migratory birds. It was invented by Henrik Mouritsen and Barrie Frost in the early 21st century [Mouritsen, Frost, 2022], leading to a significant increase in research on monarch orientation and navigation over the following two decades. Now, flight simulators in various modifications are used not only in studies on monarch butterflies but also on other insects, including European butterflies [Nesbit et al., 2009; Pakhomov et al., 2023, 2025], hoverflies [Massy et al. 2022], and moths [Dreyer et al, 2018; 2025 Hui et al, 2023].
A design of our flight simulator
Guides:
- How to create classical version of a flight simulator:
A behavioral assay to test sensory-cue-guided oriented flight in monarch butterflies under controlled conditions - How to use a flight simulator to study migratory insects:
A Guide for Using Flight Simulators to Study the Sensory Basis of Long-Distance Migration in Insects - Non-invasive tethering technique:
Assaying lepidopteran flight directionality with non-invasive methods that permit repeated use and release after testing
The flight simulator is constructed from non-magnetic materials (PVC, aluminium, PETG) and consisted of three main components:
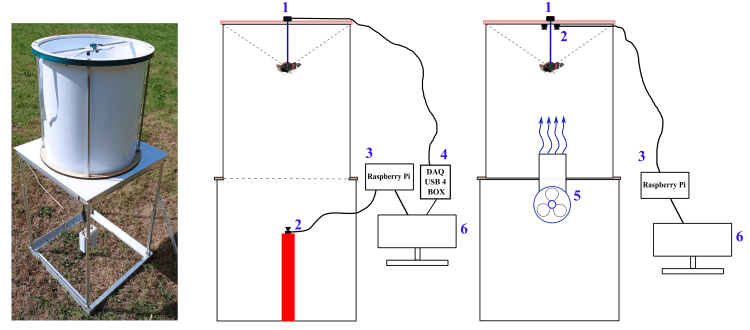
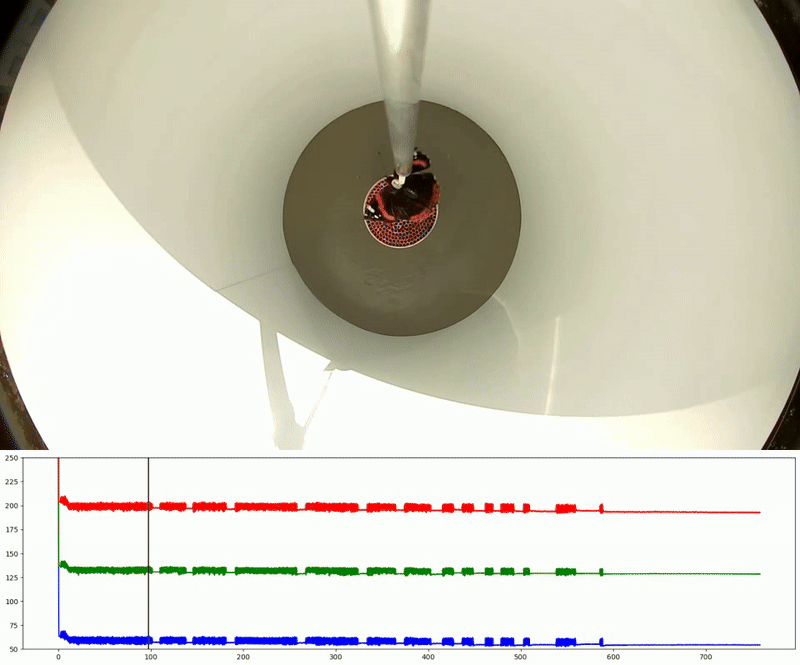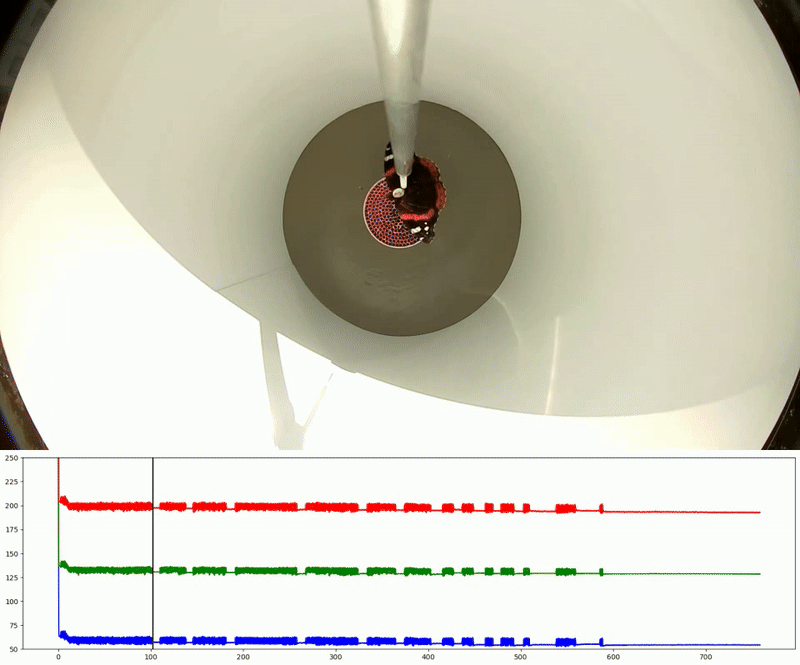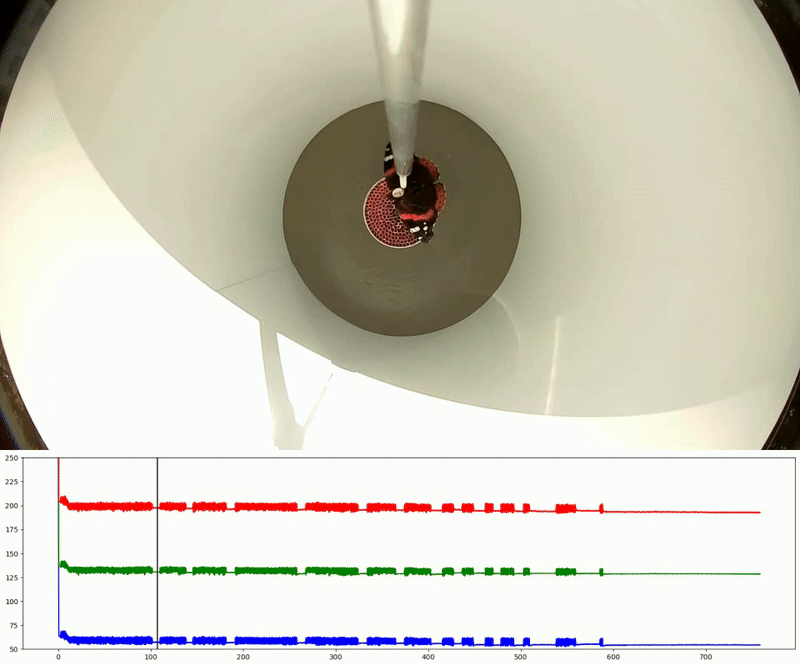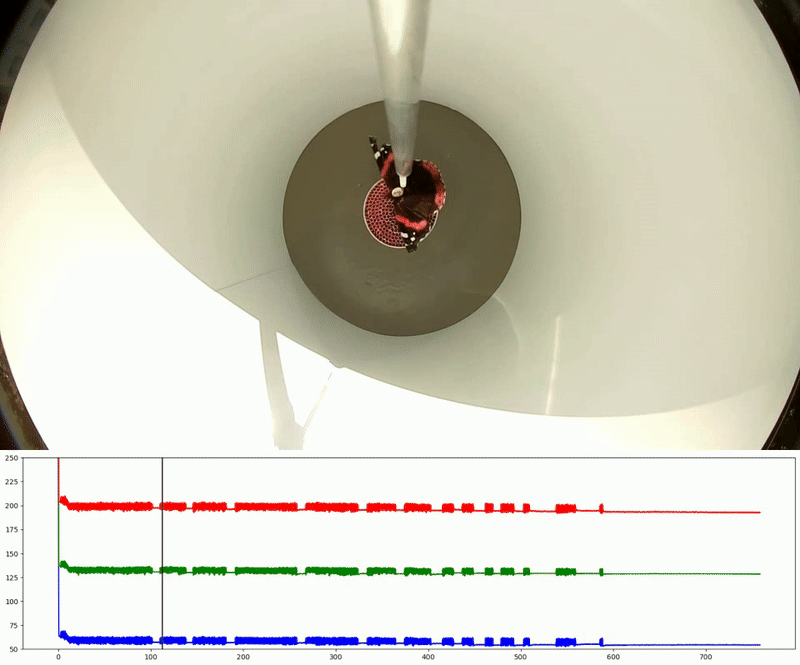
Flight Chamber – A white plastic cylinder (45 cm in diameter, 50 cm in height) is placed vertically on a plastic/aluminium table. At the centre of the table, a 120-mm diameter 3D-printed plastic pipe (5), perforated with hundreds of 3-mm holes, create a laminar airflow (≤ 1 m/s). This airflow, generated by a PWM-controlled computer fan, is designed to stimulate tethered butterflies into active flight (Mouritsen & Frost, 2002). Most components are designed using Autodesk Fusion 360 for for fabrication via laser-cutting and 3D printing.
Butterfly Attachment System – A non-magnetic rod is mounted on top of the cylinder, with an encoder at its centre. A fine tungsten rod (15 cm long, 0.5 mm in diameter) serve as the encoder shaft, connecting to the encoder (1). To facilitate quick and secure attachment, a small plastic tube (20 mm in length, 2 mm in diameter, with a 0.5 mm hole) is affixed to the distal end of the rod. All procedures are non-invasive and do not harm the butterflies or moths; after testing, they are released in good body and wing condition and can continue their migration.
Video Recording System – The system records insect flight for behavioural and orientation analysis using using DeepLabCut or custom-written scripts. In the classical version, an optical encoder (1) is used for this purpose.
Two miniature video cameras (2; Waveshare Electronics, model H) are symmetrically positioned around the tungsten rod, with one capturing the butterflies’ behaviour from above. Using two cameras instead of one ensure a symmetrical environment within the flight simulator. A Raspberry Pi 4 single-board computer (3) connected to a laptop (6) is used for real-time monitoring of insect flight behaviour and to store raw video footage from each test for further analysis.
Various types of information about the migratory flight of an insect in a flight simulator can be extracted from video files, including , activity patterns (flight/non-flight), and.
flight tracks
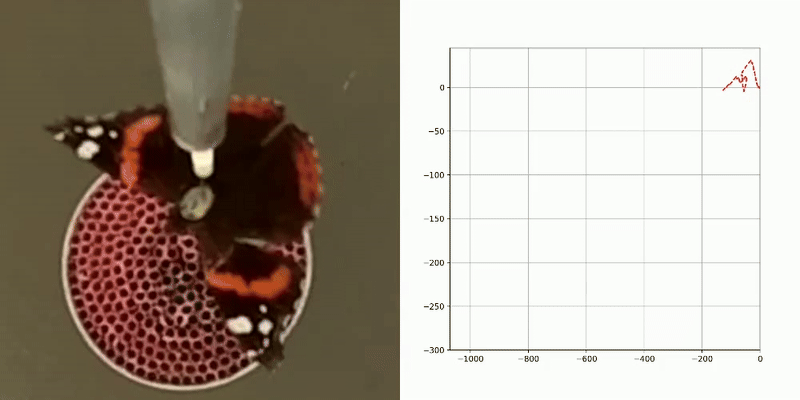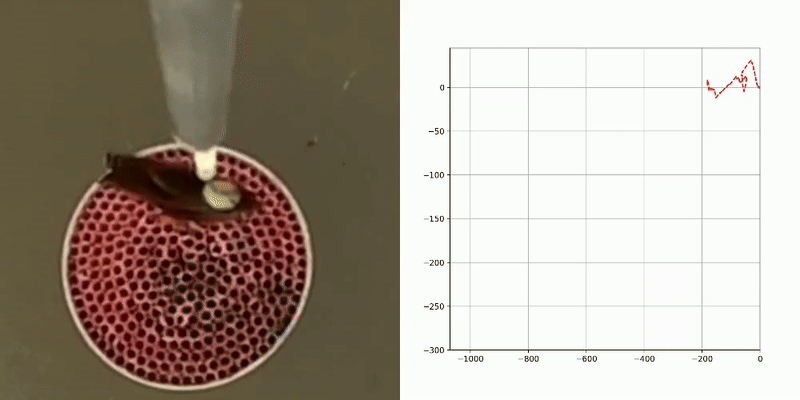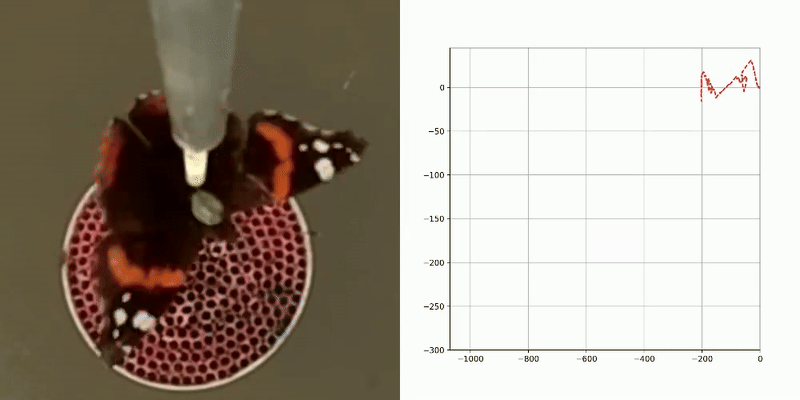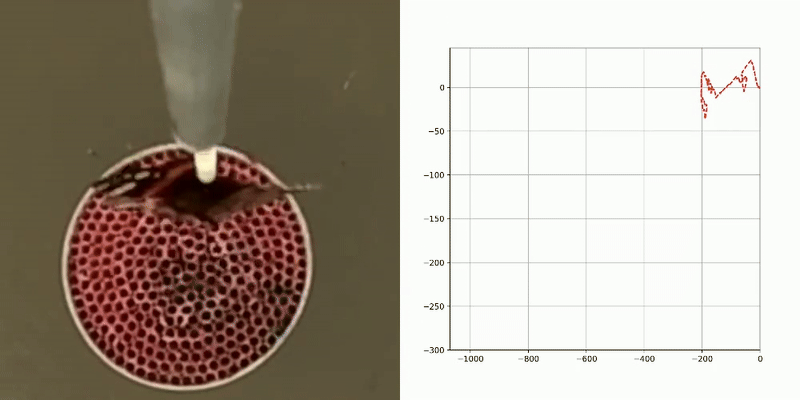
activity patterns
flight direction
custom-written neural network
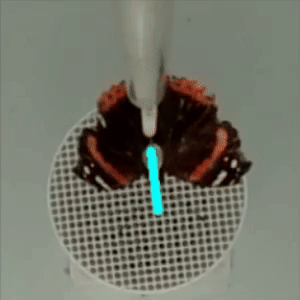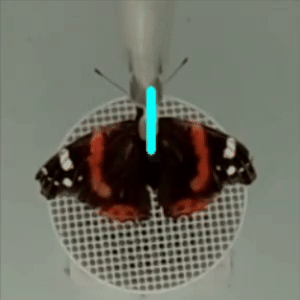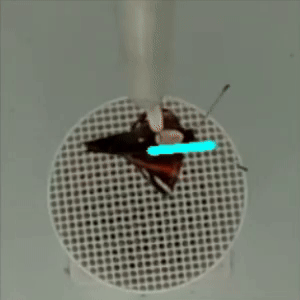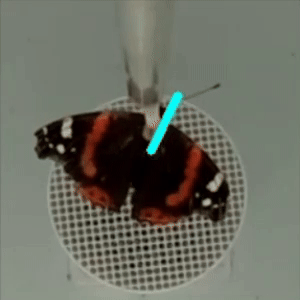
in DeepLabCut
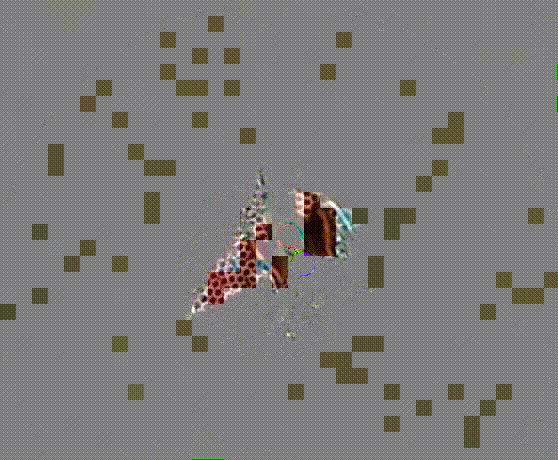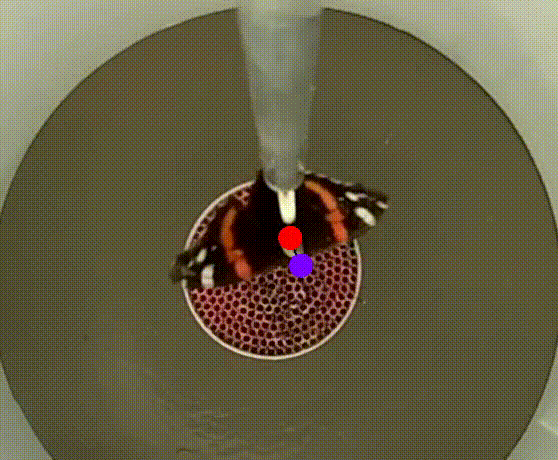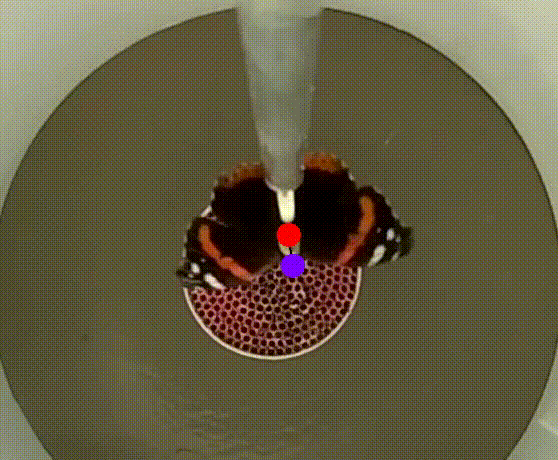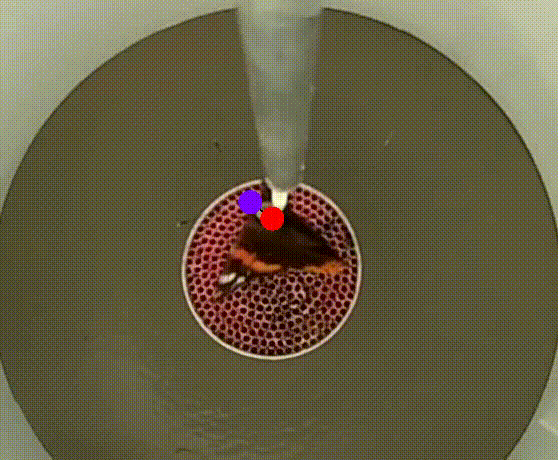
Main components, price, where to buy
| Part of simulator | Component | Quantity | Price (GBP) | Link | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Videorecording system | Video camera | 2 | 28 | RobotShop (UK) | |
| 2 | 24 | PiHut | alternative | ||
| Main computer (raspberry pi) | 1 | 43 | PiHut | Raspberry Pi 3 or 4 | |
| Camera cable | 1 | 5 | PiHut | For Rasp Pi 3 and 4, Rasp Pi 5 – 50 cm cable only | |
| Encoder system | E4T encoder | 1 | 20 | US Digital | |
| Encoder cable (3 m) | 1 | 22 | US Digital | ||
| DAQ device | 1 | 475 | US Digital | ||
| Flying chamber | Clear acrylic tube (450 mm OD) | 1 | 690 | Plastock | Price for 2.1 m tube = 4 cylinders |
| Custom-made cylinder | 1 | ~ 180 | Different suppliers | white plastic sheets, wooden rods, and two laser-cut clear acrylic circles | |
| Plastic tabletop with a central hole for a fan | 1 | 50 | Local laser-cut company | created in Autodesk Fusion 360 | |
| Air fan tube | 1 | custom-made and 3D printed | created in Autodesk Fusion 360 | ||
| Computer PWM fan | 1 | 28 | Amazon | Silent fan powered via USB from power bank + fan speed controller | |
| Network | 5V Splitter | 1 | 8 | Amazon | If you need to connect several Raspberry PIs to one laptop (power bank powered, no need electricity) |
| Part of simulator | Component | Quantity | Price (GBP) | Link | Comments |
